Chemical Level of Organization-A Tutorial & Self Assessment
Levels of Organization:
Chemical level:
□ Simplest level (smallest components) includes atoms &
molecules
□ Building blocks of matter
Organelles:
□ Atoms & molecules assemble to form specialized
structures within the cell with a variety of shapes, sizes, &
functions
□ Includes: nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes
Cellular level:
□ Composed of a variety of different organelles that
assemble together. Basic structural & functional unit of an
organism. Same common function, vary in size & shape,
each type having its own unique function.
□ Includes: muscle cells, nerve cells, blood cells
Tissue level:
□ Groups of similar cells that have a common function.
□ Includes: Epithelial tissue, Connective tissue, Muscle
tissue, Nervous tissue
Organ level:
□ Composed of two or more different types of tissues. They
perform specific functions and have defined shapes.
□ Includes: Stomach, brain, heart, lungs
Organ system level:
□ Made of two or more different but related organs that have
a common function
□ Includes: Digestive system, Cardiovascular system
Organism level:
□ The sum total of all structural levels working together.
Levels of Structural Organization in the human: taking a more profound look:
The human body has 6 main levels of structural organization. We will begin this lesson with the simplest level within the structural hierarchy.
Chemical level– is the simplest level within the structural hierarchy. The chemical level includes the tiniest building blocks of matter, atoms, which combine to form molecules, like water. In turn, molecules combine to form organelles, the internal organs of a cell.
Cellular level– the cellular level is made up of the smallest unit of living matter, the cell. Individual cells may have some common functions but vary widely in size and shape. Each type of cells carries out a set of unique tasks within the human body.
Tissue level– Tissues are groups of similar cells that have a common function. A tissue must contain two different types of cells. The four basic tissue types in humans include epithelium, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Each tissue has a characteristic role within the human body which we will discuss later.
Organ level– an organ is a structure composed of at least two different tissue types that perform a specific function within the body. Examples include the brain, stomach, and liver. Complex functions begin to emerge at this level.
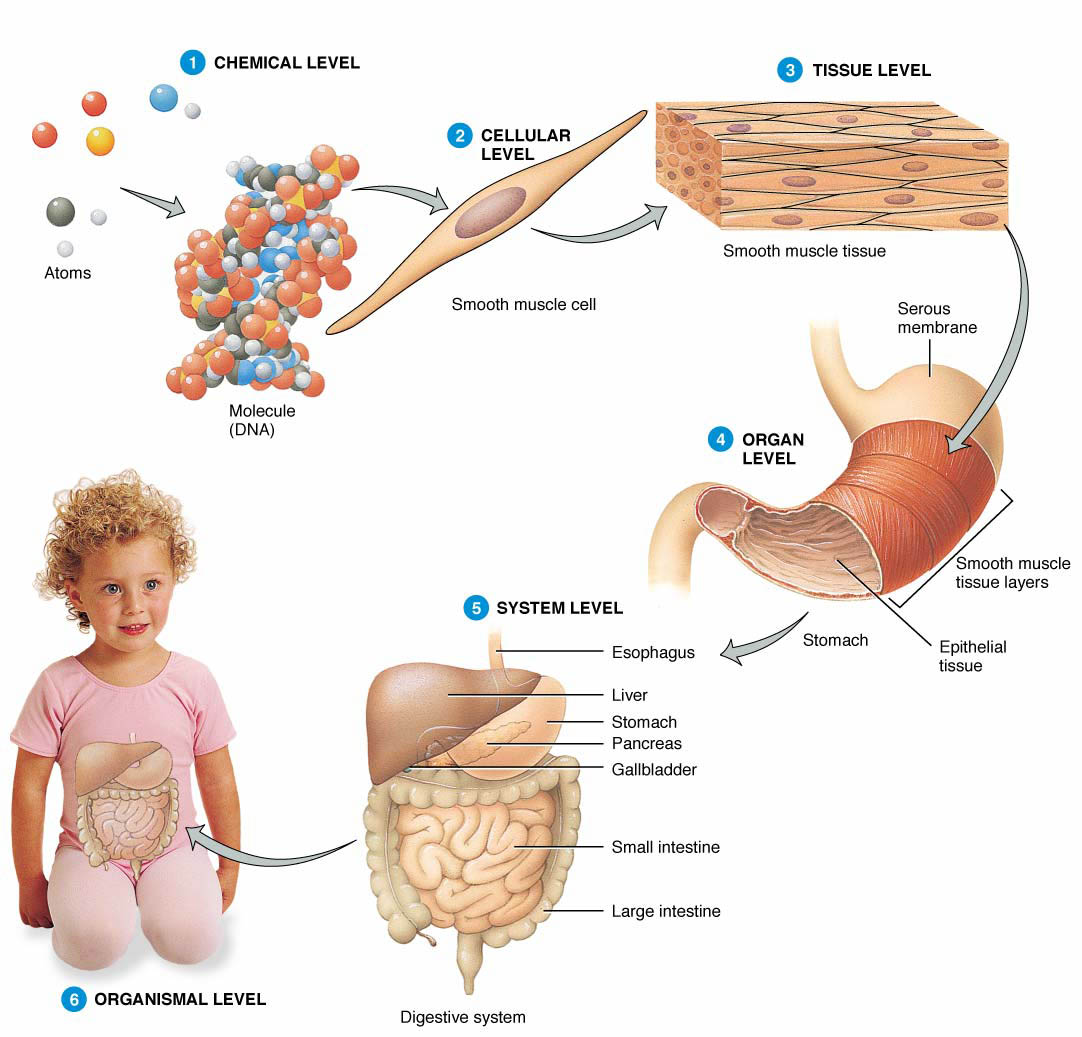
Levels of structural organization that make up the human body.
Organ system level– One or more organs work in unison to accomplish a common purpose. For instance, the heart and blood vessels work together and circulate blood throughout the body to provide oxygen and nutrients to cells. Besides the cardiovascular system, the other organ systems of the body are the integumentary, skeletal, nervous, muscular, endocrine, respiratory, lymphatic, digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Organismal level– The organismal level is the highest level of organization. It is the sum total of all structural levels working together. In short, it is the human being (or organism) as a whole.
Review
- Name the six different levels of structural organization in the human body and explain their relationships.
- List the 11 organ systems of the human body and explain their major functions.Check your understanding
- In the hierarchy, at which level of structural organization would a cytologist’s field of study be considered?
- What is the correct structural order of the following terms: atom, organ, cell, organism, tissue?
- Which organ system includes the heart and blood vessels? Which organ system includes the kidneys?
So….
on on
Structural Organization of the Human Body
By the end of this section, you will be able to: •Describe the structure of the human body in terms of six levels of organization•List the eleven organ systems of the human body and identify at least one organ and one major function of each
Before you begin to study the different structures and functions of the human body, it is helpful to consider its basic architecture; that is, how its smallest parts are assembled into larger structures. It is convenient to consider the structures of the body in terms of six fundamental levels of organization that increase in complexity: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism ([link]).

Levels of Structural Organization of the Human Body
The organization of the body often is discussed in terms of six distinct levels of increasing complexity, from the smallest chemical building blocks to a unique human organism.This illustration shows biological organization as a pyramid. The chemical level is at the apex of the pyramid where atoms bond to form molecules with three dimensional structures. An example is shown with two white hydrogen atoms bonding to a red oxygen atom to create water. The next level down on the pyramid is the cellular level, as illustrated with a long, tapered, smooth muscle cell. At this level, a variety of molecules combine to form the interior fluid and organelles of a body cell. The next level down is the tissue level. A community of similar cells forms body tissue. The example given here is a section of smooth muscle tissue, which contains many smooth muscle cells closely bound side by side. The next level down is the organ level, as illustrated with the bladder and urethra. The bladder contains smooth muscle while the urethra contains skeletal muscle. These are both examples of muscle tissues. The next level down is the organ system level, as illustrated by the entire urinary system containing the kidney, ureters, bladder and urethra. At this level, two or more organs work closely together to perform the functions of a body system. At the base of the pyramid is the organismal level illustrated with a woman drinking water. At this level, many organ systems work harmoniously together to perform the functions of an independent organism.
The Six Levels of Organization
To study the chemical level of organization, scientists consider the simplest building blocks of matter: atoms and molecules. All matter in the universe is composed of one or more unique pure substances called elements, familiar examples of which are hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, calcium, and iron. The smallest unit of any of these pure substances (elements) is an atom. Two or more atoms combine to form a molecule, such as the water molecules, proteins, and sugars found in living things. Molecules are the chemical building blocks of all body structures.
A cellis the smallest independently functioning unit of a living organism. Even bacteria, which are extremely small, independently-living organisms, have a cellular structure. Each bacterium is a single cell. All living structures of human anatomy contain cells, and almost all functions of human physiology are performed in cells or are initiated by cells.
A human cell typically consists of flexible membranes that enclose cytoplasm, a water-based cellular fluid together with a variety of tiny functioning units called organelles. In humans, as in all organisms, cells perform all functions of life. A tissueis a group of many similar cells (though sometimes composed of a few related types) that work together to perform a specific function. An organis an anatomically distinct structure of the body composed of two or more tissue types. Each organ performs one or more specific physiological functions. An organ systemis a group of organs that work together to perform major functions or meet physiological needs of the body.
This book covers eleven distinct organ systems in the human body ([link]and [link]). Assigning organs to organ systems can be imprecise since organs that “belong” to one system can also have functions integral to another system. In fact, most organs contribute to more than one system.
Organ Systems of the Human Body
Organs that work together are grouped into organ systems.This illustration shows eight silhouettes of a human female, each showing the components of a different organ system. The integumentary system encloses internal body structures and is the site of many sensory receptors. The integumentary system includes the hair, skin, and nails. The skeletal system supports the body and, along with the muscular system, enables movement. The skeletal system includes cartilage, such as that at the tip of the nose, as well as the bones and joints. The muscular system enables movement, along with the skeletal system, but also helps to maintain body temperature. The muscular system includes skeletal muscles, as well as tendons that connect skeletal muscles to bones. The nervous system detects and processes sensory information and activates bodily responses. The nervous system includes the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves, such as those located in the limbs. The endocrine system secretes hormones and regulates bodily processes. The endocrine system includes the pituitary gland in the brain, the thyroid gland in the throat, the pancreas in the abdomen, the adrenal glands on top of the kidneys, and the testes in the scrotum of males as well as the ovaries in the pelvic region of females. The cardiovascular system delivers oxygen and nutrients to the tissues as well as equalizes temperature in the body. The cardiovascular system includes the heart and blood vessels.
Organ Systems of the Human Body (continued)
Organs that work together are grouped into organ systems.The lymphatic system returns fluid to the blood and defends against pathogens. The lymphatic system includes the thymus in the chest, the spleen in the abdomen, the lymphatic vessels that spread throughout the body, and the lymph nodes distributed along the lymphatic vessels. The respiratory system removes carbon dioxide from the body and delivers oxygen to the blood. The respiratory system includes the nasal passages, the trachea, and the lungs. The digestive system processes food for use by the body and removes wastes from undigested food. The digestive system includes the stomach, the liver, the gall bladder (connected to the liver), the large intestine, and the small intestine. The urinary system controls water balance in the body and removes and excretes waste from the blood. The urinary system includes the kidneys and the urinary bladder. The reproductive system of males and females produce sex hormones and gametes. The male reproductive system is specialized to deliver gametes to the female while the female reproductive system is specialized to support the embryo and fetus until birth and produce milk for the infant after birth. The male reproductive system includes the two testes within the scrotum as well as the epididymis which wraps around each testis. The female reproductive system includes the mammary glands within the breasts and the ovaries and uterus within the pelvic cavity.
The organism level is the highest level of organization. An organismis a living being that has a cellular structure and that can independently perform all physiologic functions necessary for life. In multicellular organisms, including humans, all cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems of the body work together to maintain the life and health of the organism.
Chapter Review
Life processes of the human body are maintained at several levels of structural organization. These include the chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism level. Higher levels of organization are built from lower levels. Therefore, molecules combine to form cells, cells combine to form tissues, tissues combine to form organs, organs combine to form organ systems, and organ systems combine to form organisms.
Review Questions
The smallest independently functioning unit of an organism is a(n) ________.
1.cell
2.molecule
3.organ
4.tissue
ANS. 1
A collection of similar tissues that performs a specific function is an ________.
1.organ
2.organelle
3.organism
4.organ system
ANS. 1
The body system responsible for structural support and movement is the ________.
1.cardiovascular system
2.endocrine system
3.muscular system
4.skeletal system
ANS. 4
CRITICAL THINKING QUESTIONS
Name the six levels of organization of the human body.
Chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organism.
The female ovaries and the male testes are a part of which body system? Can these organs be members of more than one organ system? Why or why not?
The female ovaries and the male testes are parts of the reproductive system. But they also secrete hormones, as does the endocrine system, therefore ovaries and testes function within both the endocrine and reproductive systems.
Measure Your Understanding Question and Answer: