Immune System & Lymphatic System
BIO 240 Review Lymphatic System
At A Glance!
You might not like cleaning, but your lymphatic system does! Your lymphatic system is a network of vessels and body parts that collect fluids that leak out of your cells and blood. I bet you didn’t know you had leaks inside of you!
Your body is mostly water and other fluids. In fact, it’s more than 60% water. Most of this fluid is found in your cells and blood, but some gets out. Your lymphatic system sweeps up the leaked fluid and returns it to your bloodstream. If it didn’t clean up these leaks, the fluid would build up in your body tissues, and you’d swell up like a balloon. Your lymphatic system also helps your immune system, which we’ll learn about later in this lesson.
How It Works
Your lymphatic system is made up of lymph vessels, lymph nodes and organs. At the ends of your lymph vessels are lymph capillaries. You can think of lymph capillaries as little vacuum cleaners because their job is to pick up leaked fluids.
The lymph capillaries pass the fluid along to the lymph vessels. All of your lymph vessels travel toward your neck. When they arrive, they dump the fluid into large veins so the fluid can get back into your bloodstream.
Lymph Nodes
As the lymph fluid travels toward your neck, it passes through lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small collections of tissue shaped like beans, and they’re part of your immune system. They remove bacteria and other bad cells from the lymph fluid. Lymph nodes also make white blood cells, which are the good guys of your immune system. They make antibodies that hunt down disease-causing cells in your body.
You have hundreds of lymph nodes in your body. Clusters of them can be found in your thighs, armpits and neck. Did your doctor ever feel your neck when you had a sore throat? The doctor was feeling for swollen lymph nodes. Sometimes, your lymph nodes swell when they’re busy fighting off an infection.
Lymph Organs
The body also has a set of lymph organs whose job is to support the lymphatic system. Let’s explore some of the major lymph organs.

Please refer to lesson and Label the following:
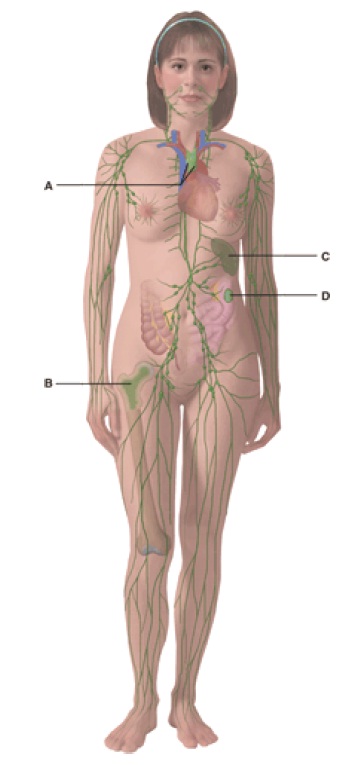


-
1.
Which of the following is not a function of the lymphatic and immune system?
- A.
Draining excess interstitial fluid
- B.
Maintaining water homeostasis in the body
- C.
Transporting dietary lipids
- D.
Carrying out immune responses
- A.
-
2.
What is the major difference between lymph and interstitial fluid?
- A.
Composition of electrolytes
- B.
White blood cells are present in lymph
- C.
Location
- D.
Types of proteins present
- E.
Red blood cells are present in interstitial fluid
- A.
-
3.
Lack of resistance is also known as:
- A.
Pathogenic
- B.
Innate
- C.
Specific
- D.
Susceptibility
- E.
Lymphatic
- A.
-
4.
What causes lymph from the small interstines to appear white?
- A.
Proteins
- B.
WBC
- C.
RBC
- D.
Lipids
- E.
Fats
- A.
-
5.
Which of the following is not considered an organ of the immune system?
- A.
Spleen
- B.
Lymph node
- C.
Red bone marrow
- D.
Thymus
- E.
Pancreas
- A.
-
6.
The left subclavian vein receives lymph from
- A.
Left axillary vein
- B.
Lumbar trunk
- C.
Jugular trunk
- D.
Thoracic duct
- E.
Right lymphatic duct
- A.
-
7.
The lymph from the right foot empties into the
- A.
Left axillary vein
- B.
Lumbar trunk
- C.
Jugular trunk
- D.
Thoracic duct
- E.
Right lymphatic duct
- A.
-
8.
The skeletal muscle and respiratory pumps are used in
- A.
Lymphatic system
- B.
Cardiovascular system
- C.
Immune system
- D.
Lymphatic and immune systems
- E.
Lymphatic, immune and cardiovascular systems
- A.
-
9.
Which of the below produces the hormone that promotes maturation of T cells?
- A.
Spleen
- B.
Lymph node
- C.
Red bone marrow
- D.
Thymus
- E.
Pancreas
- A.
-
10.
In the thymus, where is it speculated that T cels die?
- A.
Capsule
- B.
Trabeculae
- C.
Epithelial cells
- D.
Hasall’s corpuscles
- E.
T cells do not die in the thymus
- A.
-
11.
This portion of the lymph node does not contain any lymphatic nodules.
- A.
Inner cortex
- B.
Outer cortex
- C.
Medulla
- D.
Sinuses
- E.
Trabeculae
- A.
-
12.
Which of the following is a function of the spleen?
- A.
Removese worn out blood cells
- B.
Circulates lymph
- C.
Cleanses interstitial fluid
- D.
Cleanses lymph
- E.
Traps microbes with mucus
- A.
-
13.
Which of these does NOT provide a physical or chemical barrier?
- A.
Macrophages
- B.
Saliva
- C.
Urine
- D.
Mucus
- E.
Stratified squamous epithelium
- A.
-
14.
Which of these provides a non-specific cellular disease resistance mechanism?
- A.
Macrophages
- B.
T lymphocytes
- C.
B lymphocytes
- D.
Memory B cells
- E.
Stratified squamous epithelium
- A.
-
15.
These anti-microbial substances will diffuse to uninfected cells and reduce production of viral proteins.
- A.
Transferrins
- B.
Perforins
- C.
Complement proteins
- D.
Defensins
- E.
Interferons
- A.
-
16.
These anti-microbial substances promote cytolysis, phagocytosis and inflammation.
- A.
Transferrins
- B.
Perforins
- C.
Complement proteins
- D.
Defensins
- E.
Interferons
- A.
-
17.
These are mainly used to kill infectious microbes and tumour cells.
- A.
Natural killer cells
- B.
Perforins
- C.
Mucus
- D.
Platelets
- E.
Antimicrobial proteins
- A.
-
18.
Which of the following is NOT a sign of inflammation?
- A.
Redness
- B.
Pain
- C.
Heat
- D.
Mucus production
- E.
Swelling
- A.
-
19.
Which of the following intensifies the effect of interferons and promotes the rate of repair?
- A.
Complement proteins
- B.
Perforin
- C.
Fever
- D.
Macrophages
- E.
Natural killer cells
- A.
-
20.
Which of the below do NOT induce vasodilation and permeability (increased fluid flow) to an infection site?
- A.
Histamines
- B.
Kinins
- C.
Perforin
- D.
Leukotrienes
- E.
Complement proteins
- A.
-
21.
When B and T cells are fully developed and mature, they are known to be
- A.
Immunocompetent
- B.
Pluripotent stem cells
- C.
Primary lymphatic cells
- D.
Specifically promoted
- E.
Germ cells
- A.
-
22.
This induces production of a specific antibody.
- A.
Phagocytosis
- B.
Antigen
- C.
Antibody
- D.
Defensin
- E.
Immunoglobulin
- A.
-
23.
This can only stimulate an immune response if attached to a larger carrier molecule.
- A.
Epitope
- B.
Antigen
- C.
Hapten
- D.
MHC
- E.
CD8
- A.
-
24.
Which of the following is responsible for diversity in the immune system?
- A.
Antigen receptors
- B.
MHC
- C.
Hapten
- D.
MHC and antigen receptors
- E.
Epitopes
- A.
-
25.
This class of cels includes macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells.
- A.
Antigen presenting cells
- B.
Primary lymphocytes
- C.
T cells
- D.
RBC
- E.
Epitope cells
- A.
-
26.
This can only become activiated when bound to a foreign antigen and simultaneously receiving a costimulate.
- A.
B cell
- B.
T cell
- C.
Interferon
- D.
MHC
- E.
Antigen presenting cell
- A.
-
27.
These display CD 4 in their membrane and are associated with MHC class II molecules.
- A.
Cytotoxic T cells
- B.
Helper T cells
- C.
Memory T cells
- D.
MHC
- E.
B cells
- A.
-
28.
T cells secrete this toxin that is used to fragment DNA.
- A.
Perforin
- B.
Tumour antigen
- C.
Interferons
- D.
Lymphotoxin
- E.
Toxin T
- A.
-
29.
This class of antibodies is mainly found in sweat, tears, breast milk and GI secretions.
- A.
IgG
- B.
IgA
- C.
IgM
- D.
IgD
- E.
IgE
- A.
-
30.
This will lead to inflammation, enahancement of phagocytosis and bursting of microbes.
- A.
Classical complement system
- B.
Alternative complement system
- C.
Apoptosis
- D.
Classical and alternative complement systems
- E.
Hapten activation
- A.
-
31.
This action makes microbes more susceptible to phagocytosis.
- A.
Opsonization
- B.
Cytolysis
- C.
Inflammation
- D.
Comlement
- E.
Hybridoma
- A.
-
32.
This is a self-responsive cell that is inactive.
- A.
Deleted cell
- B.
Hybridoma cell
- C.
Epitopic cell
- D.
Anergy cell
- E.
Natural killer cell
- A.
-
33.
In the diagram, where do pluripotent stem cells come from?
- A.
A
- B.
B
- C.
C
- D.
D
- E.
None of the above
- A.
-
34.
In the diagram, where do T cells mature?
- A.
A
- B.
B
- C.
C
- D.
D
- E.
None of the above
- A.
-
35.
In the diagram, what is comprised of white and red pulp?
- A.
A
- B.
B
- C.
C
- D.
D
- E.
None of the above
- A.
-
36.
In the diagram this vessel drains lymph from the upper right side of the body into venous blood using a subclavian vein.
- A.
B
- B.
C
- C.
F
- D.
G
- E.
E
- A.
-
37.
In the diagram these are the bronchomediastinal trunks.
- A.
A and F
- B.
B and G
- C.
C and H
- D.
D and I
- E.
E and J
- A.
-
38.
In the diagram, what are the principle trunks?
- A.
All of the labeled areas are principle trunks
- B.
A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H
- C.
A, B, D, E, F, G, H, I
- D.
A, B, D, E, F, G, I, J, K
- E.
A, B, D, H, I, J, K
- A.
-
39.
In the diagram, this consists of a medulla, medullary sinus and reticular fibres.
- A.
B
- B.
C
- C.
D
- D.
E
- E.
F
- A.
-
40.
In the diagarm, cells found in this region include B cells, follicular dendritic cells and macrophages.
- A.
B
- B.
C
- C.
D
- D.
E
- E.
F
- A.
-
41.
In the diagram, cells found in this region include B cells, plasma cells and macrophages.
- A.
B
- B.
C
- C.
D
- D.
E
- E.
None of the above
- A.
-
42.
This is characterized by the inability of the immune system to protect the body from a pathogen.
- A.
Immunodeficiency diseases
- B.
Allergy
- C.
Autoimmune disease
- D.
Transplantations
- E.
Graft
- A.
-
43.
An acute allergic response can lead to:
- A.
Transplantation
- B.
Retroviruses
- C.
Anaphylactic shock
- D.
Passive immunity
- E.
Active immunity
- A.
-
44.
A natural exposure to an infectious agent leads to:
- A.
Passive immunity
- B.
Active immunity
- C.
Passive and active immunity
- D.
None of the above
- A.
-
45.
This class of antibodies is produced after an initial exposure to antigens.
- A.
IgA
- B.
IgE
- C.
IgM
- D.
IgD
- E.
IgG
- A.
-
46.
Of the following which is considered the body’s second major defense?
- A.
Mucous cells
- B.
Germ cells
- C.
Lymphocytes
- D.
Natural killer cells
- E.
None of the above
- A.
-
47.
Lymphocytes can recognize
- A.
Self cells
- B.
Foreign cells
- C.
B cells
- D.
T cells
- E.
Natural killer cells
- A.
-
48.
In B cell receptors, the light/heavy variable regions are located here:
- A.
Transmembrane region
- B.
Tips of the molecules
- C.
There is no variable region on a B cell receptor
- D.
Depends on the type of B cell
- E.
There are only constant regions
- A.
-
49.
What is the most polymorphic molecule in the immune system?
- A.
Lymphocytes
- B.
Monocytes
- C.
MHC
- D.
WBC
- E.
RBC
- A.
-
50.
The primary response will peak how many days after an exposure?
- A.
1 day or less
- B.
2-7 days
- C.
10-17 days
- D.
20-30 days
- E.
Over a month
- A.
-
51.
Which type of immunity defends against any type of invader?
- A.
Nonspecific
- B.
Specific
- C.
Cell mediated
- D.
Antibody mediated
- E.
None of the above
- A.
-
52.
This is the ability of an antigen to react specifically with the antibodies or cells it has provoked.
- A.
Specificity
- B.
Immunogenicity
- C.
Reactivity
- D.
Epitopes
- E.
Immune response
- A.
-
53.
This is a small hormone that can stimulate or inhibit many normal cell functions.
- A.
Enzyme
- B.
Kinins
- C.
Cytokine
- D.
MHC
- E.
Leukocyte
- A.