Tutorial Assignment Self Assessment-Part I (Modules I-III) and Part II Modules IV and V
Tutorials Assignment-Self Assessment-Part I (Modules I-III) and Part II Modules IV and V
Forward Mention:
Please be advised that you do not have to do this assignment. This assignment is an opportunity for those students who are interested in improving their status in the class and/or overall understanding of the course material. If you do wish to participate, this assignment, that is fine.
You refer to the information provided to you in class notes, assigned pages of reading in you text book, and the content, videos and diagrams provided to you within this site to assist you with this assignment MUST be handed in within the first 15 minutes of the next class, 02/21. Please understand that the assignment MUST BE COMPLETE and their will be no exceptions.
>I Introduction to A & P & Chemical Levels of Organization
>II Cells
>III Tissues
>IVOrgans >V Organ Systems
Module I Introduction to A & P & Chemical Level of Organization
Overview and Warm Up:
- Gross anatomy b. Histology c. Cytology d. Embryology
- Which of the following disciplines is LEAST likely to require the use of a microscope? a. Gross anatomy b. Embryology c. Histology d. Cytology
- During the process of cell division there are several phases. During one of them the nucleus is split “apart” or split “up” into 2 separate portions. Based on your knowledge of word roots, which of the following terms refers to this phase? ` a. Interphase b. Anaphase c. Gammaphase d. Metaphase e. Prophase
- In class we discussed the hierarchical arrangement of the human body. Arrange the following structures according to that plan from the simplest to the most complex.1. Oxygen molecule 2. Respiratory system 3. Mitochondria 4. Trachea
- Pseudostratified columnar epithelium 6. Goblet cell
- 1,6,3,4,5,2 b. 2,4,5,6,1,3 c. 1, 3,6,5,4,2 d. 3,1,5,6,4,2 e. 1,6,3,2,5,4
- Which of the following organ systems functions in communication and control?
- Muscular b. Cardiovascular c. Nervous d. Spinocerebral e. Reproductive
- Which of the following is TRUE about humans?
- We are vertebrates and we are bipedal. b. We have mammary glands and a total of 6 middle ear bones.
- We have a large brain size to body size ratio. d.We are considered to be mammals, primates, and hominids.
- All of the above
- Which of the following is an example of negative feedback?
- Control of blood pressure b. Control of blood glucose c. Control of body temperature
d.Control of blood pH e. All of the above
| 8. _____________ investigates the body’s structure, whereas __________ investigates the processes or functions of living things. | ||||
| A) | Physiology, cytology | |||
| B) | Physiology, anatomy | |||
| C) | Anatomy, histology | |||
| D) | Histology, cytology | |||
| E) | Anatomy, physiology | |||
| 9. The study of tissues is called | ||||
| A) | cytology. | |||
| B) | anatomy. | |||
| C) | histology. | |||
| D) | anatomic imaging. | |||
| E) | physiology. | |||
| 10. Ultrasound, X-rays, CT, and MRI are all examples of | ||||
| A) | anatomic imaging. | |||
| B) | surface anatomy. | |||
| C) | regional anatomy. | |||
| D) | gross anatomy. | |||
| E) | cytology. | |||
| 11. A group of cells with similar structure and function, together with the extracellular substances located between them, form a(n) | ||||
| A) | organism. | |||
| B) | organelle. | |||
| C) | tissue. | |||
| D) | organ. | |||
| E) | organ system. | |||
| 12. The basic living unit of all plants and animals is the | ||||
| A) | cell. | |||
| B) | chemical. | |||
| C) | organ. | |||
| D) | organelle. | |||
| E) | tissue. | |||
| 13. Which organ system removes substances from the blood, combats disease, maintains tissue fluid balance, and absorbs fat from the digestive tract? | ||||
| A) | endocrine | |||
| B) | integumentary | |||
| C) | lymphatic | |||
| D) | respiratory | |||
| E) | urinary | |||
| 14. Which organ system consists of hormone-secreting glands, such as the pituitary and thyroid glands? | ||||
| A) | endocrine | |||
| B) | integumentary | |||
| C) | lymphatic | |||
| D) | respiratory | |||
| E) | urinary | |||
| 15. Which of these characteristics of life helps maintain homeostasis when environmental conditions change? | ||||
| A) | growth and development | |||
| B) | metabolism | |||
| C) | organization | |||
| D) | reproduction | |||
| E) | responsiveness | |||
| 16. Development is a process that begins with fertilization and ends with | ||||
| A) | birth. | |||
| B) | adolescence. | |||
| C) | adulthood. | |||
| D) | old age. | |||
| E) | death. | |||
| 17. Given these terms related to negative-feedback: 1. control center 2. effector 3. receptor 4. response 5. stimulus Arrange them in the correct order as they operate to maintain homeostasis. | ||||
| A) | 1,2,3,4,5 | |||
| B) | 2,3,5,1,4 | |||
| C) | 3,2,1,5,4 | |||
| D) | 4,5,3,2,1 | |||
| E) | 5,3,1,2,4 | |||
| 18. body temperature of 98.6 degrees F (37 degrees C) is the __________ for body temperature. | ||||
| A) | constant | |||
| B) | lower limit | |||
| C) | normal range | |||
| D) | set point | |||
| E) | upper limit | |||
| 19. Which of these processes illustrates positive-feedback? | ||||
| A) | increase in respiratory rate during exercise | |||
| B) | increase in heart rate when blood pressure decreases | |||
| C) | shivering when body temperature decreases | |||
| D) | increase in uterine contractions when uterine stretching increases during childbirth | |||
| E) | all of these | |||
| 20. Failure of negative-feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis | ||||
| A) | may produce disease. | |||
| B) | occurs when blood pressure increases during exercise. | |||
| C) | can be corrected by stimulating positive-feedback mechanisms. | |||
| D) | cannot be corrected by medical therapy. | |||
| E) | all of these | |||
| 21. According to the concept of negative feedback, a slight increase in blood pressure causes | ||||
| A) | an increase in heart rate. | |||
| B) | a decrease in heart rate. | |||
| C) | no change in heart rate. | |||
| 22. To maintain homeostasis, the normal range of values for a variable | ||||
| A) | is always below the set point. | |||
| B) | may change in different situations. | |||
| C) | may not deviate from the set point. | |||
| D) | occurs because of positive-feedback. | |||
| 23. A term that means “away from the midline” is: | ||||
| A) | distal | |||
| B) | lateral | |||
| C) | medial | |||
| D) | proximal | |||
| E) | superior | |||
| 24. Which of these descriptions does NOT apply correctly to a person in the anatomic position? | ||||
| A) | standing erect | |||
| B) | head facing forward | |||
| C) | feet facing forward | |||
| D) | arms hanging to the side | |||
| E) | palms facing toward the thighs | |||
| 25. The scapula (shoulder blade) is __________ to the lung. | ||||
| A) | dorsal | |||
| B) | posterior | |||
| C) | superficial | |||
| D) | all of these | |||
| 26. The elbow is __________ to the wrist. | ||||
| A) | distal | |||
| B) | inferior | |||
| C) | lateral | |||
| D) | medial | |||
| E) | proximal | |||
| 27. The nose is __________ and __________ to the ears. | ||||
| A) | anterior, proximal | |||
| B) | superior, lateral | |||
| C) | inferior, posterior | |||
| D) | anterior, medial | |||
| E) | superficial, medial | |||
| 28. Which of the paired terms below are opposites? | ||||
| A) | anterior and cephalic | |||
| B) | posterior and cephalic | |||
| C) | posterior and caudal | |||
| D) | superior and cephalic | |||
| E) | anterior and dorsal | |||
| 29. Pancreatitis describes | ||||
| A) | inflammation of the pancreas. | |||
| B) | removal of the pancreas. | |||
| C) | cancer of the pancreas. | |||
| D) | secretions from the pancreas. | |||
| E) | death of the pancreas. | |||
| 30. A person lying flat on his back is said to be in the __________ position. | ||||
| A) | anatomic | |||
| B) | prone | |||
| C) | supine | |||
| 31, Given these directional terms: 1. caudal 2. cephalic 3. distal 4. inferior 5. proximal Which of these directional terms correctly describes the relationship of the ankle to the knee? | ||||
| A) | 1,3 | |||
| B) | 1,3,4 | |||
| C) | 2,3,4 | |||
| D) | 3,4 | |||
| E) | 4,5 | |||
| 32. Which of these anatomical terms refers to the ankle? | ||||
| A) | crural | |||
| B) | femoral | |||
| C) | carpal | |||
| D) | pedal | |||
| E) | tarsal | |||
| 33. Which of these anatomical terms refers to the shoulder? | ||||
| A) | acromial | |||
| B) | brachial | |||
| C) | cervical | |||
| D) | clavicular | |||
| E) | digital | |||
| 34. The only plane that can divide the body into equal halves is the | ||||
| A) | frontal (coronal) plane. | |||
| B) | oblique plane. | |||
| C) | midsagittal plane. | |||
| D) | transverse plane. | |||
| E) | Serengeti plane. | |||
| 35. A(n) __________ plane divides the body into superior and inferior portions. | ||||
| A) | frontal (coronal) | |||
| B) | oblique | |||
| C) | sagittal | |||
| D) | transverse | |||
| 36. A cut across the long axis of an organ made at other than a right angle is called a(n) | ||||
| A) | cross section. | |||
| B) | transverse section. | |||
| C) | oblique section. | |||
| D) | longitudinal section. | |||
| 37. In which quadrant of the abdomen would stomach pain most likely be felt? | ||||
| A) | lower left | |||
| B) | lower right | |||
| C) | upper left | |||
| D) | upper right | |||
| 38. Which of these structures is NOT found in the mediastinum? | ||||
| A) | diaphragm | |||
| B) | esophagus | |||
| C) | heart | |||
| D) | thymus gland | |||
| E) | trachea | |||
| 39. Which of these statements concerning body regions is correct? | ||||
| A) | The pelvis is located between the thorax and abdomen. | |||
| B) | The leg extends from the knee to the ankle. | |||
| C) | The arm extends from the shoulder to the wrist. | |||
| D) | The trunk can be divided into the thorax and pelvis. | |||
| E) | The thorax is often subdivided superficially into four quadrants. | |||
| 40. The cavity surrounded by the rib cage and bounded inferiorly by the diaphragm is the | ||||
| A) | mediastinum. | |||
| B) | pericardial cavity. | |||
| C) | thorax. | |||
| D) | abdomen. | |||
| E) | pelvic cavity. | |||
| 41. The lungs are separated by the | ||||
| A) | mediastinum. | |||
| B) | mesenteries. | |||
| C) | diaphragm. | |||
| D) | peritoneal membranes. | |||
| E) | pelvic cavity. | |||
| 42. Serous membranes | ||||
| A) | line body cavities that open to the outside. | |||
| B) | produce a lubricating film of fluid. | |||
| C) | are found only on the walls of the thoracic cavity. | |||
| D) | separate the abdominal cavity from the pelvic cavity. | |||
| E) | completely cover retroperitoneal organs. | |||
| 43. The serous membrane on the surface of the lungs is called | ||||
| A) | parietal pericardium. | |||
| B) | visceral pericardium. | |||
| C) | parietal pleura. | |||
| D) | visceral pleura. | |||
| E) | parietal peritoneum. | |||
| 44. Which of these organs are in retroperitoneal cavity? (Check all that apply) | ||||
| A) | adrenal glands | |||
| B) | kidneys | |||
| C) | urinary bladder | |||
| D) | spleen | |||
| E) | pancreas | |||
| 45. Given these serous membranes: 1. parietal pericardium 2. visceral pericardium 3. parietal peritoneum 4. visceral peritoneum 5. parietal pleura 6. visceral pleura A man had a knife wound that penetrated the abdomen, passed through the stomach, and hit the diaphragm, but did not pass all the way through. Arrange the serous membranes in the correct order as the knife passed through them. | ||||
| A) | 1,2,4,3,5 | |||
| B) | 2,3,4,4,3,2 | |||
| C) | 3,4,4,3 | |||
| D) | 4,3,3,4,5 | |||
| E) | 5,6,6,4 | |||
| Bonus Question: The Integumentary System consists of:___________________________________________ | ||||
Module I: Introduction to A & P and Chemical Organization of Life.
46) What is structure of the body referred to as: _______________________
47) What is the process of functions of living things referred to as: _______________________
48) When you are standing straight, facing forward, arms at sides with palms forward, what is this position referred to as? _______________________
49) When you are lying face upward, what is this called? _______________________
50) When you are lying face downward, what is this referred to as? _______________________
51) What is it called when you are referencing, towards the head, upper? _______________________
52) What is another term for the superior part of the body? _______________________
53) What is it called when referencing away from head, below? _______________________
54) What is another term for the inferior part of the body? _______________________
55) The forehead is __________ to the nose? _______________________
56) Referencing towards the front, in front of? _______________________
57) What is another term for the anterior part of the body? _______________________
58) Referring to towards the back, behind? _______________________
59) What is another term for the posterior part of the body? _______________________
60) The heart is __________ to the sternum. _______________________
61) Referring to towards the midline of the body, on the inner side_______________________
62) Referencing to away from the midline of the body, on the outer side_______________________
63) Referring to between a more medial and a more lateral structure? _______________________
64) The eye is _______ to the bridge of the nose. _______________________
65) The terms proximal and distal are used for ______________ only. _______________________
66) Referencing closer to the point of limb attachment_______________________
67) Referencing farther from the point of limb attachment_______________________
68) The elbow is __________ to the wrist. _______________________
69) The Andomin is diving into ___________________ quadrants and __________________ regions.
70) Another name for dorsal is ___________________________
71) Referencing close to surface of body____________________?
72) Referencing towards interior of body? _______________________
73) Shoulder to elbow is referred to as?__________________________
74) Elbow to wrist is referred to as? _______________________
75) Hip to knee is referred to as? _______________________
76) Knee to ankle si referred to as? _______________________
77) The thorax,abdomen and pelvis make up the ______ of the body. _______________________
78) Making up the main axis of the body (head, neck, trunk) refers to? _______________________
79) Consisting of appendages or limbs_______________________
80) Another name for Frontal? _______________________
81) Orbital refers to? _______________________
82) Buccal refers to? _______________________
83) Sternal pertains to? _______________________
84) Pectoral Refers to? _______________________
85) Mammary refers to? _______________________
86) Thoracic refers to? _______________________
87) Umbilicus refers to? _______________________
88) Cervical refers to: _______________________
89) What does antecubital mean? _______________________
90) What does Antebrachial refer to? _______________________
91) What does axillary refer to? _______________________
92) What does acromial refer to? _______________________
93) What does pollex mean? _______________________
94) What does the term palmar refer to? _______________________
95) Whats does the term coxal refer to? _______________________
96) What does the term inguinal refer to? _______________________
97) What does the term patellar refer to? _______________________
98) What does the term Crural refer to? _______________________
99) What does the term Peroneal refer to? _______________________
100) Body cavity encasing the brain and spinal cord? _______________________
101) Body cavity surrounded by the ribs and chest muscles. _______________________
102) Body Cavity that houses the lungs? _______________________
103) The Mediastinum contains/consists of: _______________________
cavity surrounded by abdominal muscles and pelvic girdle.
104) Body cavity that contains stomach, liver, spleen, intestines, etc… _______________________
105) Body Cavity that contavins bladder, some reproductive organs, rectum… _______________________
106) large, dome-shaped muscle separating the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities. _______________________
107) What is the thin, double-layered membrane lining body cavities and surrounding internal organs referred to as? _______________________
108) Another name for serous membrane. _______________________
109) The part of the membrane lining cavity walls_______________________
110) The part of the membrane covering the organs_______________________
111) Lubricating fluid between the parietal and visceral serosa is referred to as: _______________________
112) Body cavity/cavities that contains mouth, teeth, tongue, interior of digestive organs, anus_______________________
113) Body Cavity that houses the eyes_______________________
114) List at least 5 Organs of the Trunk_______________________
115) Explain each of the following “Characteristics of Life”.
- a) Organization, _______________________
- b) Metabolism, _______________________
- c) Responsiveness, _______________________
- d) Growth, _______________________
- e) Development, _______________________
- f) Reproduction, _______________________
- g) Respiration, _______________________
- h) Absorption, _______________________
- i) Circulation, _______________________
- j) Assimilation, _______________________
- k) Excretion _______________________
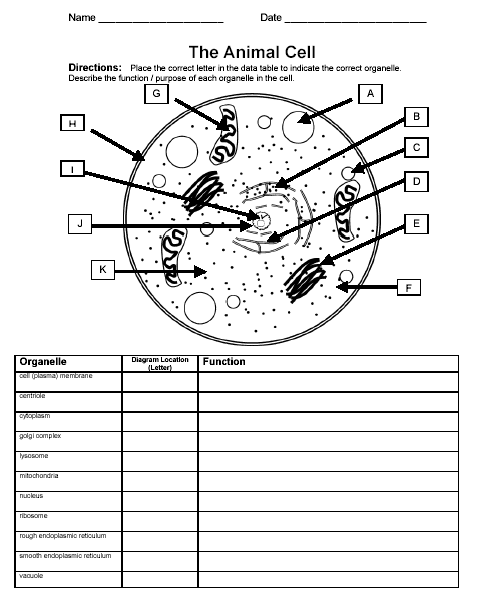
Module II CELLS
116) What is Made up of a phospholipid bilayer – phospholipids arrange themselves so that they hydrophilic heads are facing ECF and ICF, while the hydrophobic tails face inward toward each other. Separates ECF from ICF? _______________________
117) What is ECF stand for? _______________________
118) What does ICF Stand for? _______________________
119) Longer than cilia. Used for locomotion. Unique to Sperm? _______________________
120) Responsible for protein synthesis. Made up of small and large ribosomal subunit. (rRNA) Ribosomes can be free or fixed. Also some are anchored to the Rough ER? _______________________
121) Extends from the nuclear envelope that surrounds the nucleus and out into the cytoplasm. Forms a network of tubes that extend out into the cell called cisternae? _______________________
122) Has fixed ribosomes attached to the outer surface, which gives it a rough texture. Ever changing, always attached to nucleus. Primary function; protein synthesis, transport and store protein? _______________________
123) What is cilia? _______________________
124) What are microfilaments? _______________________
125) Has no ribosomes associated with it. Primary function; lipid and carbohydrate synthesis? _______________________
126) Shipping and receiving, very fluid; parts break free, sometimes stay in cell and create lysosomes? _______________________
127) The organelle responsible for “Garbage Disposal”_______________________
128) The powerhouse; makes ATP. Have their own DNA and ribosomes, so they are capable of reproduction within the cell. Only inherited from mother? _______________________
129) Surrounded by nuclear envelope. Double membrane. Two phospholipid bilayers. Protects DNA? _______________________
130) Synthesizes ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Can have multiple? _______________________
131) Stored within nucleus. Genetic code that is inherited from our parents? _______________________
132) Passive. “Downhill” High to low concentration until equilibrium. Down in concentration gradient is referred to as? _______________________
133) Active. Transport of molecules in/out of cell via vesicles from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration via a semi permeable membrane if referred to as? _______________________
134) Osmolarity/Osmotic concentration? Answer: Total concentration of solutes. _______________________
135) Osmotic pressure: Answer: The measure of the tendency of water to move across a membrane. It can be measured as the force required to stop osmotic flow.
136) What is Tonicity: Answer How the solute concentration of a solution affects a cell.
137) What is an Isotonic solution: Answer: Same solute concentration. Passive
138) What is a Hypotonic solution: Answer: Low concentration. More in than out.
139) What is a Hypertonic solution: Answer More out than in.
140) Lyse: Answer: Cell swells and might burst.
141) Crenation: Answer: Cell shrinkage.
142) Facilitated diffusion: Answer: Integral protein carrier on the cell membrane must bind the solute to transfer it through the cell membrane. Substances are still moving down a concentration gradient (no ATP, Passive). Substances that use this method are insoluble to lipids and too large to fit through the membrane.
143) Active transport: Answer: This type of movement requires energy to move an ion into an area of higher concentration. Active (Needs ATP).
144) Ion pumps: Answer: Carrier proteins that expand energy to move an ion into an area of higher concentration.
145) Exchange pumps: Answer: Sodium potassium exchange pump. 3 sodium ions move out of cell while 2 potassium ions move in. Active (Needs ATP). May use up to 40% of resting cells ATP supply. Constantly operating.
146) Secondary active transport: Answer: The movement of one substance down it’s concentration gradient while simultaneously moving another substance against it’s concentration gradient; does not initially require ATP.
147) Endocytosis: Answer: Packaging of extracellular substances within a vesicle at the cell membrane for import into cell.
148) Pinocytosis: Answer: Pino-Drinking. The cell folds the membrane inward to take in a large volume of extracellular materials. Not as specific as receptor mediated endocytosis.
149) Phagocytosis: Answer: Phago-Eating(solid). Only performed by select cells such as macrophages. Cytoplasmic extension called pseudopodia surrounds an object and engulfs it. More specific.
150) Exocytosis: Answer: A vesicle created inside the cell fuses with the membrane to discharge its components out into the ECF. Example; saliva, sweat, neurotransmitters, digestive hormones, enzymes, etc.
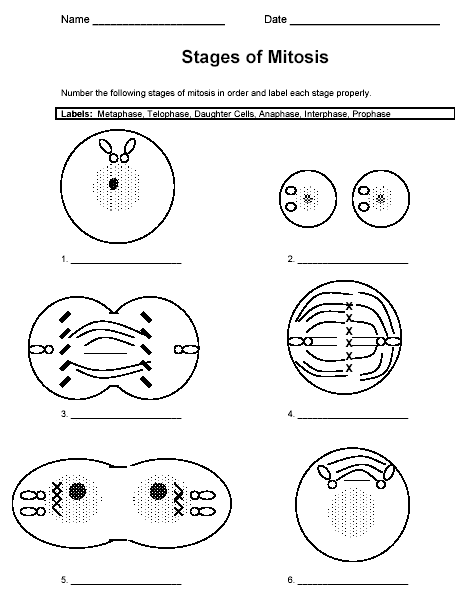
151) Interphase
Answer: G1 (first gap phase.) S (Synthesis phase). G2 (Second gap phase.)
152) G1 phase
Answer: Cell spends most of its life. The length of time varies depending upon the cell type. Normal cell activities are performed such as growth and protein synthesis.
153) S phase
Another pair of centrioles is manufactured. DNA replication occurs.
154) G2 Phase
Answer: Short phase prior to actual division of DNA. Enzymes needed for division are manufactured. Success of DNA replication is assessed. Errors can be corrected before proceeding. (DNA Mutation)
155) Prophase
Answer: Chromatin condenses; chromosomes become visible. Nuclear envelope breaks down. Pairs of centrioles migrate to opposite ends of the cell.
156) Metaphase
Answer: Chromosomes are present at the equator. Mitotic spindle is fully formed.
157) Anaphase
Answer: Centromere breaks apart. Each chromatid (now called daughter chromosome) is pulled to opposite poles as motor proteins in the kinetochore break down the spindle fibers.
158) Telophase
Answer: Telo=End. Chromosomes reach opposite poles. Rough ER manufacturers 2 new nuclear envelopes. Chromosomes uncoil into chromatin. Mitotic spindle breaks down and disappears. Nucleoli appear signaling the production of RNA to assist with protein synthesis.
159) Cytokinesis
Answer: Division of the cytoplasm. Cleavage furrow created as motor proteins interact with cytoskeletal components.
160) When cells divide too rapidly
Answer: Cancer develops.
161) Metastasis
Answer: Cells create a tumor that can travel to other locations in the body.
Module III Tissues
162. Which of the following is NOT one of the four main types of tissues?
A. basement
B. epithelial
C. connective
D. muscle
163. Which type of tissue is designed to stretch?
A. stratified
B. squamous
C. transitional
D. epthelial
164. Tissues are groups of similar cells working together to:
A. increase the size and mass of structures in the body
B. perform common functions
C. fight against diseases
D. deliver messages
165. This type of tissue is composed of scattered cells that form a matrix:
A. macrophages
B. cuboidal
C. nervous
D. connective
166. Adipose tissue is also known as:
A. fat
B. cartilage
C. areolar tissue
D. brain matter
167. Smooth muscle is found mainly in:
A. the heart
B. the stomach
C. the brain
D. the skeletal system
168. Chondrocytes are cells found in:
A. the small intestine
B. the heart
C. the brain
D. cartilage
169. What structure connects bones to other bones?
A. tendons
B. hyaline cartilage
C. ligaments
D. fibroblasts
170. Psuedostratified tissue has a distinctive appearance because:
A. the nuclei of individual cells do not line up perfectly
B. cilia is attached to the surface of the cells
C. cells are square and formed in perfect blocks
D. cells are square in the bottom layer and flat at the top
171. Elastic fibers are found where in the body?
A. joints
B. vocal cords
C. ear and nose
D. heart
172. Which of the following are the mail four tissue types below
a. simple, epithelial, nerve, connective, lymph
b. aquamous, cubodial, columnar, transitional
c. squamous, tubes, sac, digestive
d. simple, stratified, transitional, columnar
173. single layer of cells is also known as what type of arrangement?
a. simple
b. layered
c. stratified
d. none of the above
174. multi layered cells are also known as what type of arrangement?
a. simple
b. stratified
c. both a and b
d. none of the above
175. special function (s) of the skin?
a. can modify itself to make stronger
b. filters imputities
c. produces secretions
d. all of the above
176. two types of glands in the human body what are they
a. exocrine and myocrine
b. exocrine and endocrine
c. ductless and muscular
d. organs and glands
Last improved on 9/25/2010 at 3:00:52 PM
177. exocrine glands…
a. secrete through ducts or tubes
b. don’t exrete at all
c. only secrete during sleep
d. secrete in other cells
178. sebaceous glands secrete what
a. oil and sweat
b. oil
c. sweat
d. none of the above
179. secreations are what
a. horemones which effect “target organs”
b. horemones which effect eye sight
c. horemones which effect nerve impusles
d. horemones which effect “target muscles”
180. true of false connective tissue forms framework of the body, connects, and binds
a. true
b. false
181. areolar is the most common type of connective tissue and it is found where in the body?
a. blood vessles, in membranes, and in the brain
b. around blood vessels, in membranes, around vessels, and organs
c. only around vessels
d. none of the above
182. adipose tissue’s functions include…
a. insulation
b. friction reduction
c. padding, energy reserve, and insulation
d. none of the above are correct
183. tough, translucent cartilage is what type
a. hyaline
b. fibrocartilage
c. elastic
d. none of the above
184. firm and rigid describes which type of cartilage?
a. hyaline
b. fibrocartilage
c. dense
d. elastic
185. this type of cartilage springs back into shape
a. elastic
b. fibrocartilage
c. hyaline
d. all human cartilage
186. bone is cartilage with minerals and salts known as what
a. calcium and potassium
b. potassium and carbon
c. water and salt
d. calcium and phosphate
187. osteoblasts produce….
a. cartilage
b. bone
c. lymph
d. fat
188. osteocytes mature what kind of cells
a. small
b. big
c. bone
d. blood
189. serous membranes secrete what type of fluid
a. watery
b. bloody
c. both
d. none of the above
190. pleura means what
a. heart
b. lungs
c. stomach
d. legs
191. pericardium means what
a. heart
b. lungs
c. blood
d. abdomen
192. peritoneum means what
a. heart
b. lungs
c. blood
d. abdomen
193. mondomyosin is what
a. deep fascia around muscle groups
b. superficial fascia around blood vessels
c. aournd big muscle bundles
d. around small muscle fibers
194. where would you find non-keratinised epithelium tissue?
a. oesophagus
b. hair, skin and nails.
c. stomach wall
d. bladder
With Detail, briefly Discuss/Draw’Sketch characteristics of each of the following tissues:
195. Stratified squamous
196. Simple cuboidal
197. Simple columnar
198. Cardiac muscle
199. Bone
200. Skeletal muscle
Bonus 201. Adipose
Bonus 202 Fibrous connective tissue
Bonus 203 Cartliage
Bonus 204 Blood
Bonus: 205:
List one type of tissue not mentioned here between questions 195 and 204. Go on to discuss/Sketch/Draw their characteristics as well.
Tissues Run that by me one more time
| 206 | Epithelial tissue is characterized by each of these traits, except that ____________. | |||
| A) | it lacks blood vessels | |||
| B) | it functions in secretion, absorption, and excretion | |||
| C) | epithelial cells are loosely packed and have much intercellular material | |||
| D) | it is anchored to a basement membrane | |||
| 207 | Microvilli, which function to increase surface area, are more likely to be found in ____________ epithelium. | |||
| A) | simple cuboidal | |||
| B) | simple squamous | |||
| C) | transitional | |||
| D) | simple columnar | |||
| 208 | Epithelium that appears layered due to the varying levels at which nuclei are found in cells, but in reality is not layered, is _________________. | |||
| A) | transitional epithelium | |||
| B) | pseudostratified columnar epithelium | |||
| C) | stratified squamous epithelium | |||
| D) | stratified columnar epithelium | |||
| 209 | The outer layer of the skin is composed of ______________________. | |||
| A) | transitional epithelium | |||
| B) | pseudostratified columnar epithelium | |||
| C) | stratified squamous epithelium | |||
| D) | stratified columnar epithelium | |||
| 210 | The primary purpose of stratification, or layering, in epithelial tissue is for increased _____________. | |||
| A) | protection | |||
| B) | secretion | |||
| C) | absorption | |||
| D) | thickening of the basement membrane | |||
| 211 | What type of epithelium lines the urinary bladder and is capable of distention? | |||
| A) | stratified cuboidal epithelium | |||
| B) | stratified squamous epithelium | |||
| C) | transitional epithelium | |||
| D) | stratified columnar epithelium | |||
| 212 | An exocrine gland that loses small parts of its cell bodies during secretion, as is the case for the mammary gland, is further classified as a(n) ____________ gland. | |||
| A) | merocrine | |||
| B) | apocrine | |||
| C) | holocrine | |||
| D) | endocrine | |||
| 213 | Connective tissues are somewhat similar to epithelial tissues in all of these characteristics except ___________________. | |||
| A) | they have abundant intercellular material | |||
| B) | they can usually reproduce themselves | |||
| C) | they often serve more than one function | |||
| D) | they occur throughout the body | |||
| 214 | What function do fibroblasts serve in connective tissue? | |||
| A) | carry on phagocytosis | |||
| B) | secrete heparin that prevents blood clotting | |||
| C) | secrete proteins that become fibers in the connective tissue matrix | |||
| D) | release histamine associated with allergies and inflammation | |||
| 215 | Connective tissue fibers that have great tensile strength and can be found in ligaments and tendons are _________________. | |||
| A) | elastic fibers | |||
| B) | collagenous fibers | |||
| C) | reticular fibers | |||
| D) | yellow fibers | |||
| 216 | The type of cartilage found in intervertebral disks of the vertebral column is ________________. | |||
| A) | hyaline cartilage | |||
| B) | elastic cartilage | |||
| C) | yellow cartilage | |||
| D) | fibrocartilage | |||
| 217 | Choosing from the following list of connective tissues, which one consists of cells in a fluid matrix? | |||
| A) | loose connective tissue | |||
| B) | adipose tissue | |||
| C) | bone | |||
| D) | blood | |||
| 217 | Select the correct statement about bone. | |||
| A) | Bone stores, but does not release, inorganic salts. | |||
| B) | Bone cells (osteocytes) are dead in mature bone. | |||
| C) | Bone is a very metabolically active tissue. | |||
| D) | Elderly people cannot rebuild bone. | |||
| 218 | Which muscle tissue is multinucleate, voluntary, and bears striations? | |||
| A) | skeletal muscle | |||
| B) | smooth muscle | |||
| C) | multiunit smooth muscle | |||
| D) | cardiac muscle | |||
| 219 | Neuroglial cells help neurons in each of these ways, with the exception of _______________. | |||
| A) | supporting and binding nervous tissue | |||
| B) | carrying on phagocytosis | |||
| C) | playing a role in cell-to-cell communications | |||
| D) | transmitting nervous impulses | |||
| 220 | Which of the following is not one of the four major types of tissues? | |||
| A) | epithelial | |||
| B) | connective | |||
| C) | nervous | |||
| D) | skeletal muscle | |||
| 221 | The only major type of tissue specialized for movement is the _____ tissue. | |||
| A) | nervous | |||
| B) | cardiac muscle | |||
| C) | muscle | |||
| D) | connective | |||
| 222 | The cells lining blood vessels and the lung alveoli are classed as _____ epithelium. | |||
| A) | columnar | |||
| B) | stratified squamous | |||
| C) | simple squamous | |||
| D) | cuboidal | |||
| 223 | The kidney tubules are lined with _____ epithelial cells. | |||
| A) | columnar | |||
| B) | cuboidal | |||
| C) | squamous | |||
| D) | ciliated | |||
| 224 | The cells that directly and specifically secrete mucus are called _____ cells. | |||
| A) | epithelial | |||
| B) | endocrine | |||
| C) | exocrine | |||
| D) | goblet | |||
| 225 | The term _____ refers to the fact that an epithelial tissue has only one layer of cells. | |||
| A) | stratified | |||
| B) | cuboidal | |||
| C) | simple | |||
| D) | pseudostratified | |||
| 256 | One of the main functions associated with simple squamous epithelium is _____. | |||
| A) | diffusion | |||
| B) | active transport | |||
| C) | secretion | |||
| D) | absorption | |||
| 257 | What type of tissue is found on the surface of the ovaries? | |||
| A) | simple squamous | |||
| B) | simple columnar | |||
| C) | simple cuboidal | |||
| D) | stratified epithelium | |||
| 258 | The lining of the vagina is covered with _____ cells. | |||
| A) | mucus, columnar | |||
| B) | pseudostratified epithelium | |||
| C) | stratified cuboidal | |||
| D) | stratified squamous | |||
| 259 | Connective tissue is complex because it has a variety of cells and a noncellular background called a_____ surrounding them. | |||
| A) | collagen | |||
| B) | elastin | |||
| C) | mucous secretion | |||
| D) | matrix | |||
| 260 | Which of these is not a connective tissue? | |||
| A) | blood | |||
| B) | bone | |||
| C) | muscle | |||
| D) | cartilage | |||
| 261 | What type of tissue holds most organs together? | |||
| A) | adipose | |||
| B) | muscular | |||
| C) | dense connective | |||
|
|
D) | loose connective | ||
Modules IV and V
262. A group of organs that work together is referred to as:
a. Organization of Life
b. Organelle
c. Active Transport
d. System
263. A structure made up of 2 or more kinds of tissue and is organized to perform a more complex function:
a. System
b. Organelle
c. Organ
d. Cell
264. The hypothalamus, Thyroid Gland, Adrenal Gland are in what body system?
a. Reproductive
b. Respiratory,
c. Endocrine
d. Nervous System
4. The nose, lungs and Trachea are found in what body System?
a. Integumentary
b. Respiratory
c. Endocrine
d. Muscular
265. Teeth, Tongue, Liver and appendix are what kind of organs?
a. Accessory Organs
b. Muscular
c. Cardiovascular
d. Primary
Below, list organs that make up the following Body Systems. Also, list the function of each of the body systems listed.
Body System Organs Involved Functions of the Body Sydtem
266. Lymphatic System ________________________ __________________________
267Muscular system ________________________ ___________________________
268. Cardiovascular/circulatory system ______________________ _____________________
269. Skeletal System ________________________ ____________________________
270. Endocrine System ________________________ ____________________________
271. Nervous System ________________________ _____________________
272. Respiratory System ________________________ ______________________
273. Digestive System ________________________ ________________________
274. Urinary System ________________________ __________________________
275. Respiratory System ________________________ ______________________________
List Five Solid Organs
276. ______________________________
277. ______________________________
278. ______________________________
279. ______________________________
280. ______________________________
List Five Hollow Organs
281. ______________________________
292. ______________________________
283. ______________________________
284. ______________________________
285. ______________________________
287. Which system removes gaseous waste (carbon dioxide) from the blood?
-
A. Digestive
-
B. Immune
-
C. Respiratory
-
D. Nervous288.. The lungs, nose, and trachea are part of which organ system?
-
A. Digestive
-
B. Respiratory
-
C. Muscular
-
-
D. Circulatory
289. The kidneys and urethra are part of which organ system?
A. Skeletal-
B/ Digestive
-
C. Urinary
-
D. Reproductive
290. Which of the following is not part of the integumentary system?
-
A. Nails
-
B. Hair
-
C. Skin
-
D. Teeth
291. Which system supports and protects the body while giving it shape and form?
-
A. Skeletal
-
B. Reproductive
-
C. Circulatory
-
D. Nervous
292. The pituitary gland, pineal gland, and thyroid gland are part of which system?
-
A. Nervous
-
B. Endocrine
-
C. Urinary
-
D.Lymphatic
293. Which of the following is a digestive system organ?
-
A, Kidney
-
B. Thymus
-
C. Liver
-
D. Lung
294. True or False The liver is an organ of the digestive system and the largest gland in the body. In addition to performing many functions including fat metabolism, nutrient storage, and detoxification, the liver produces hormones involved in growth and platelet production. ___________T or __________F
295. Which system helps to protect the body by producing immune cells?
-
A. Lymphatic
-
B. Cardiovascular
-
C. Digestive
-
D. Respiratory
296. True or False: The lymphatic system helps to protect the body by producing and circulating lymphocytes. These white blood cells defend the body against cancerous cells, pathogens, and foreign matter. _______T ___________F
297. True or False The respiratory system enables us to breathe. In this process, carbon dioxide is exchanged for nitrogen in the lung alveoli. Carbon monoxide is expelled from the body and nitrogen is delivered to cells and tissues through blood circulation. ________T or __________F
298. Most of the nutrient absorption that takes place during digestion occurs in the ____ .
-
A. Liver
-
B. Large Intestines
-
C. Stomach
-
D. Small Intestines
299. True or False: Very little of the nutrient absorption that takes place during digestion occurs in the small intestines. Food in the small intestines is mixed with digestive juices from the pancreas and liver, which break down and release the stored nutrients. The nutrients are absorbed at times into the blood where they can be circulated throughout the bowel.
300. This system contains the largest organ of the body.
-
A. Cardiovascular
-
B. Reproductive
-
C. Integumentary
-
D. Digestive
-
-
-